In recent years, the world has seen a resurgence in sustainable farming practices, and among them, natural farming is steadily gaining recognition. As environmental concerns and the long-term health of our ecosystems continue to make headlines, more farmers and consumers are shifting towards practices that promote biodiversity, soil health, and minimal intervention.
The Origins of Natural Farming
Natural farming, while gaining momentum in recent times, is not a new concept. Its roots can be traced back to ancient agricultural traditions, particularly in India, where farming was deeply interwoven with ecological principles. Farmers relied on natural processes—nutrient recycling, crop diversity, and pest predators—to sustain productivity. Over time, as the industrialization of agriculture brought in synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, these age-old practices were sidelined.
The resurgence of natural farming as a movement was largely credited to Masanobu Fukuoka, a Japanese farmer-philosopher, whose “do-nothing farming” philosophy emphasized minimal intervention. In his seminal book The One-Straw Revolution, Fukuoka outlined a method of farming that worked in harmony with nature, emphasizing rejection of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, advocating instead for the use of natural processes to enhance soil fertility and crop health. In India, pioneers like Subhash Palekar advocated for similar principles, leading to the development of Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF), a technique that promotes chemical-free agriculture.
What Natural Farming Encompasses
Natural farming goes beyond organic farming. While both discourage synthetic inputs, natural farming takes a step further by focusing on restoring the soil’s self-sustaining abilities.
One of the fundamental tenets of natural farming is the idea of soil rejuvenation. Unlike conventional methods that deplete the soil of essential nutrients, natural farming focuses on creating an ecosystem where the soil can regenerate itself. This is achieved through the use of cover crops, mulching, crop rotation, and fostering beneficial organisms like earthworms and microbes. In turn, this process enriches the soil, ensuring that future generations of crops can thrive without the need for synthetic inputs.
Another essential aspect of natural farming is biodiversity. By encouraging a variety of plants, animals, and microorganisms to co-exist, natural farming ensures that the agricultural ecosystem is more resilient. A diverse farm is less prone to pests and diseases, as natural predators can help maintain a balance. Moreover, the presence of diverse plants supports pollinators, which are essential for the fertilization of many crops.
Natural farming is also inherently holistic. It takes into consideration the health of the entire farm system — from the soil to the plants, animals, and humans. It’s about creating a balanced, self-sustaining farm that requires minimal external input. The concept is rooted in respect for nature, with the understanding that healthy ecosystems are the foundation for healthy crops.
Why Natural Farming Is Beneficial
The benefits of natural farming extend far beyond the farm gates. For farmers, it promises reduced input costs and increased resilience against erratic weather patterns. For consumers, it ensures chemical-free produce that is rich in nutrition. On a larger scale, it contributes to environmental sustainability by improving soil health, enhancing water retention, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
As the global agriculture sector grapples with issues like soil degradation, groundwater depletion, and climate change, natural farming offers a viable solution. It not only addresses ecological concerns but also aligns with the economic needs of smallholder farmers.
India’s National Mission for Natural Farming
Recognizing the potential of natural farming, the Government of India launched the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) under the Union Budget of 2023. This initiative aims to scale up natural farming practices across the country by providing training, funding, and resources to farmers.
The mission emphasizes the integration of natural farming into India’s agricultural policies. Pilot projects across various states are demonstrating the feasibility of this model, and the government is actively promoting farmer collectives to facilitate knowledge sharing. NMNF is not just an agricultural strategy—it is a step toward achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs).
The Future of Natural Farming: A Digital Revolution
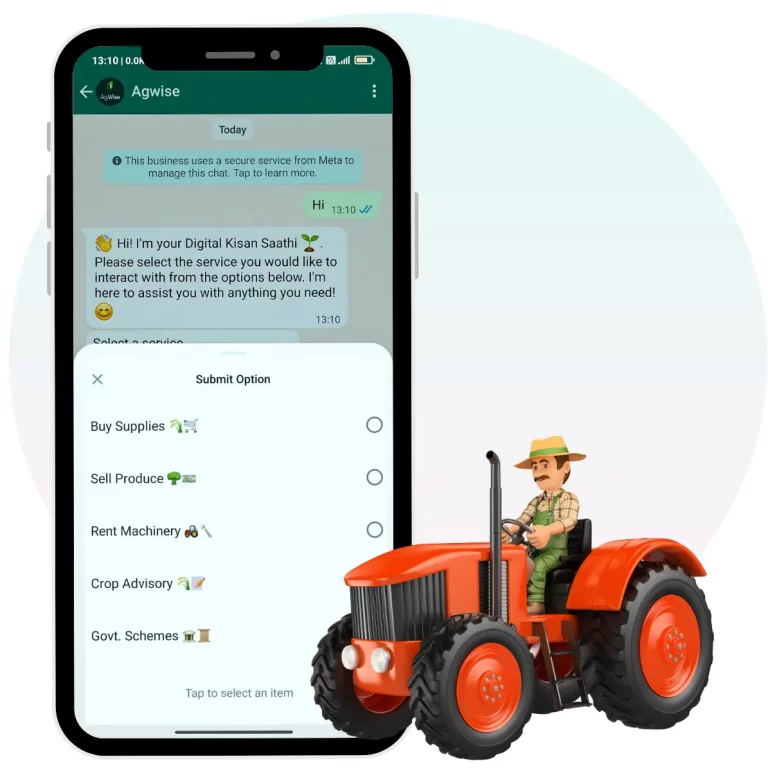
While natural farming reconnects us with traditional wisdom, the future lies in integrating these practices with modern technology. Innovations like conversational digital assistants are playing an increasingly important role in this transformation. Developmental organizations, NGOs, and agritech startups are increasingly leveraging conversational chatbots to engage with farmers and promote the adoption of natural farming practices. These AI-powered tools serve as a bridge between technical expertise and grassroots-level farming communities, providing accessible and personalized farming guidance.
Conversational chatbots are playing an increasingly important role in amplifying natural farming efforts by providing farmers with accessible and personalized support. These AI-powered tools can guide farmers through sustainable farming practices and help them implement natural farming methods effectively.
Chatbots are being leveraged to deliver natural farming training content that covers the preparation of essential natural farming solutions such as Jeevamrutha, Beejamrutha, Neemastra and many more. For instance, Farmers can receive step-by-step instructions on how to create Jeevamrutha, a natural bio-input that improves soil health, or Neemastra, a natural pesticide made from neem, which protects crops from pests without using harmful chemicals. In addition to practical recipes, chatbots can offer the hper-personalised natural farming package of practices that guides farmers to manage their farms naturally and efficiently.
Chatbots are facilitating direct connections with subject matter experts, allowing farmers to seek real-time advice on specific challenges or techniques. This easy access to expert support enhances farmers’ confidence in applying natural farming methods and helps them troubleshoot problems as they arise.
Farmers can also access digital training completion certificates, which validate their learning and knowledge in natural farming practices. These certificates not only motivate farmers but also offer advantages, such as improved credibility and access to new market opportunities.
Natural farming represents a paradigm shift in how we view agriculture—not as an extractive industry but as a symbiotic relationship with the environment. With strong governmental backing, growing farmer awareness, and the infusion of digital technologies, natural farming has the potential to transform agriculture in India.